Adapted from the 28 September UNSDSN blog by Maëlle Voil: ‘Systemic Solutions and Innovations for Climate-Resilient Regions: A look into European research program Horizon 2020 sister climate projects IMPETUS and ARSINOE’.
Today, sustainable development projects no longer revolve around the success of a specific technology. Instead, they are about promoting deep transformations by bringing different stakeholders together, and actively promoting human engagement, interdisciplinarity and learning by doing. On 19 September 2022, representatives of the sister climate projects IMPETUS and ARSINOE joined guest speakers and more than 150 online participants to explore ‘Systemic Solutions and Innovations for Climate-Resilient Regions’, in the second plenary session of the 10th Annual International Conference on Sustainable Development (ICSD 2022).
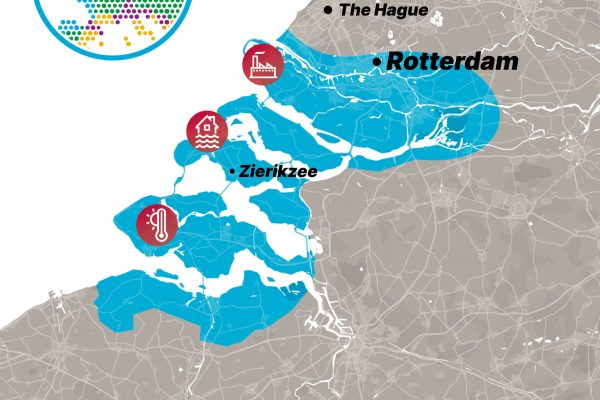
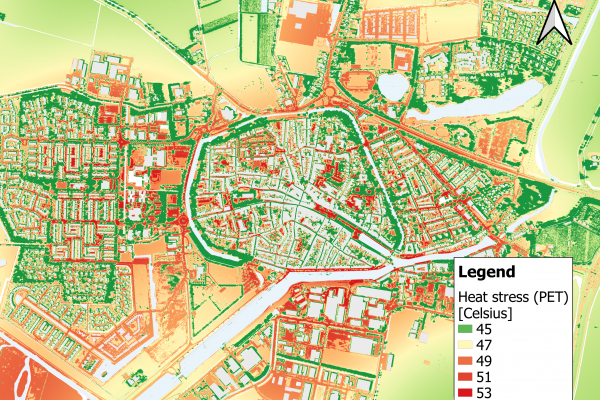
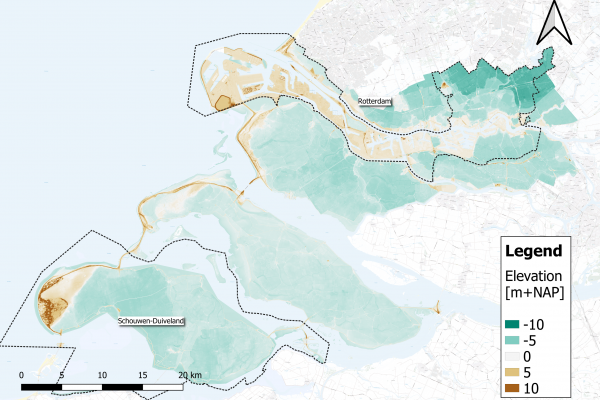
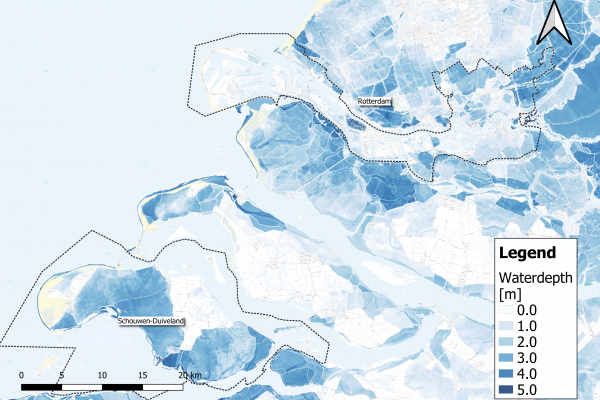
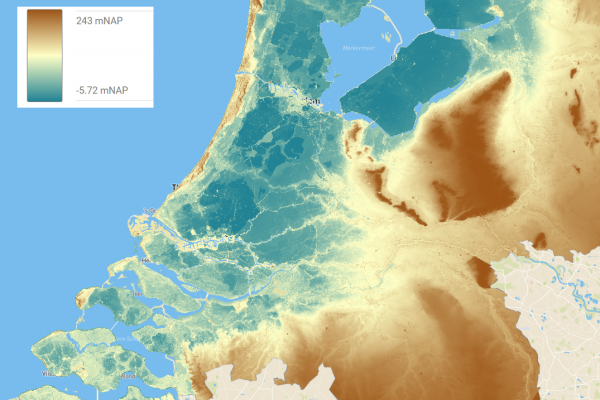
IMPETUS and ARSINOE are funded by the prestigious European research program Horizon 2020 in the Green Deal call. They explore the best pathways to climate change adaptation in different European bioclimatic regions by bringing together the most up-to-date scientific and technological advances with local knowledge and an understanding of the difficulties experienced by the communities they work with. Using advanced social engagement mechanisms combined with powerful ICT tools, they will test a combination of innovative solutions in 15 different case study demonstration sites. Their objective is to address the complex challenge of sustainable development through consensus, aiming to improve the active participation of local communities in creating solutions, knowledge and decisions about how best to adapt to climate change and mitigate its impacts.

Professor Gunter Pauli, economist, entrepreneur and author of ‘The Blue Economy’ gave an opening address calling for urgent action. The need for analysis of scientific and economic considerations to underpin careful but appealing communications to encourage action was emphasised by the panelists, who gave examples from their own areas of expertise. Dr. Aline Mosnier brought perspectives as Scientific Director of the Food, Agriculture, Biodiversity, Land-Use, and Energy (FABLE) Consortium. Civil engineering expert Professor Chrysi Laspidou of the University of Thessaly in Greece spoke for the ARSINOE project along with Dr. Martin Drews, a Senior Researcher at the Technical University of Denmark, who co-chairs the Collaborative Program on High Impact Events and Climate Change of the European Climate Research Alliance, and is a member of the Expert Advisory Group of the European Climate Risk Assessment. , Dr. Andrea Marinoni, Associate Professor of Remote Sensing at UiT The Arctic University of Norway spoke about the IMPETUS project’s approach, combining satellite data with societal information in digital tools to aid community engagement and decision making.
The session was moderated by Laura Durnford of the IMPETUS partner European Science Communication Institute (ESCI) and chaired by Andrija Erac, Manager with the Sustainable Development Solutions Network (SDSN). SDSN is a partner in the IMPETUS and ARSINOE projects and was co-organiser of this session.
- A recording of this ICSD 2022 2nd plenary session is available to view via the UNSDSN YouTube channel: view the session video.
- Read the full UNSDSN blog by Maëlle Voil.