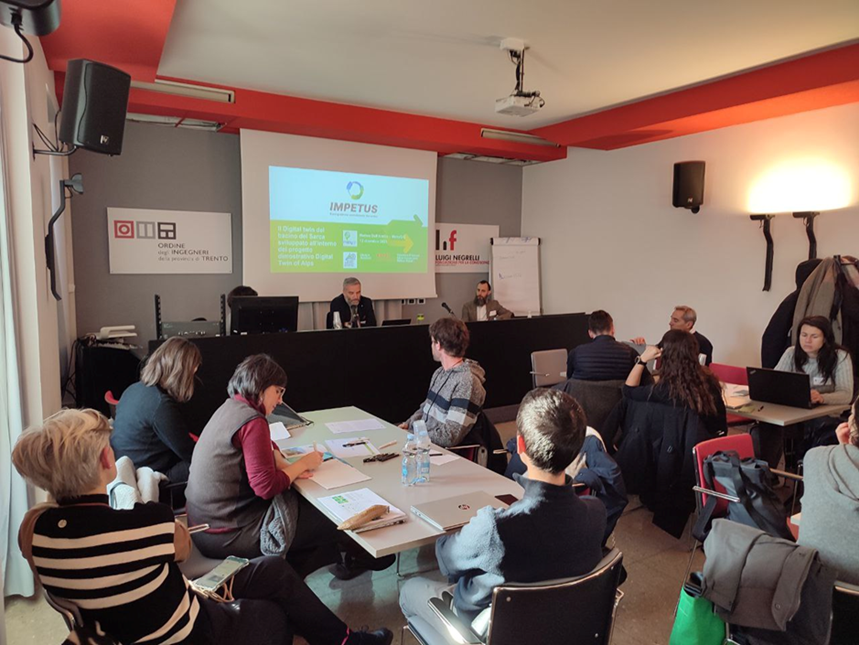
The IMPETUS project continues to make significant strides in addressing the complex challenges of water resource management, particularly in the picturesque Valle dei Laghi area. A recent workshop lead by local partners Eurac Research, MobyGIS Srl and BIM Sarca-Mincio-Garda held on December 12th, 2023, provided invaluable insights and recommendations towards the development of effective solutions for water scarcity issues.
Setting the scene
The Valle dei Laghi area is in the Province of Trento in the Italian Alps. A mosaic of mountain valleys, the area has an abundant water supply and a very fragmented population, with small villages and most municipalities having fewer than 5000 inhabitants.
Agriculture and food / wine production, hydropower production, forestry for wood fuel, slow tourism and winter ski tourism are the main economic activities. The Alps, and mountains in general, are recognised hotspots for climate change, with temperatures raising far beyond the average and more frequent extreme weather events.
Rapid climate change impacts will lead to increasing conflicts in water and land usage, for this reason IMPETUS is seeking to promote participatory approaches in decision making to ensure rapid transition to sustainable and integrated water management, biodiversity conservation and disaster risk reduction.
The IMPETUS workshop
To try and address the conflicting water needs such as irrigation, drinking water and hydropower exploitation, IMPETUS partners Eurac Research, MobyGIS Srl and BIM Sarca-Mincio-Garda in the Valle dei Laghi area have made efforts to engage with local and provincial stakeholders to gather inputs and feedback on what tools could be employed to, at least partly satisfy the needs of all affected parties.
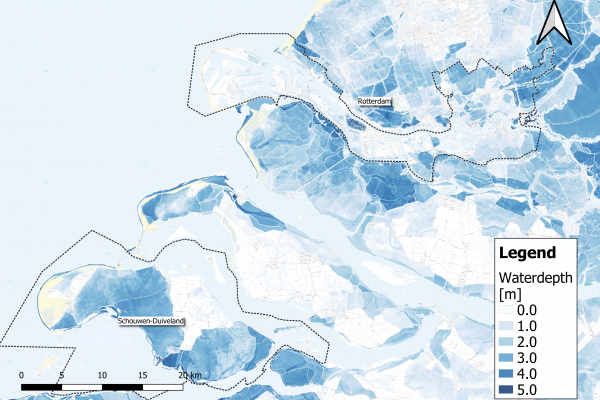
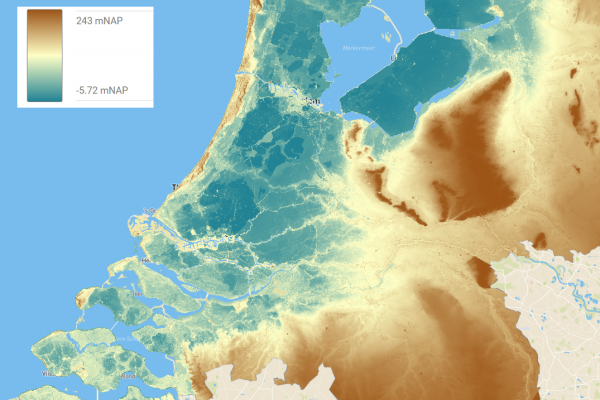
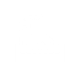
During the workshop, IMPETUS partners presented new approaches such as hydrological forecasting – a highly useful tool for anticipating the occurrence of droughts and floods – and showed a protype of the digital twin of the Sarca river basin that will lead to the co-creation and development of a comprehensive Decision Support System (DSS) for sustainable and integrated water management. In other words a resilience tool, a platform from which stakeholders can deduce possible scenarios to make the best decisions in the face of increasingly extreme climate situations and the need to navigate water scarcity issues.
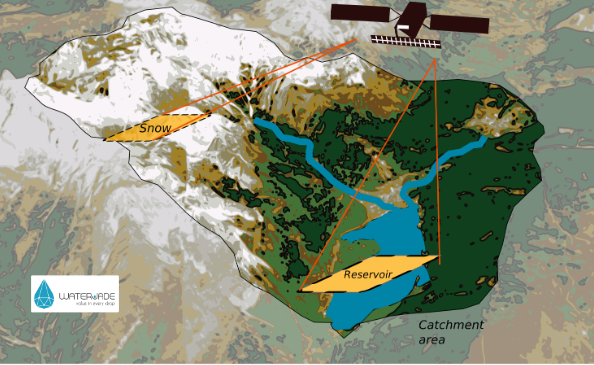
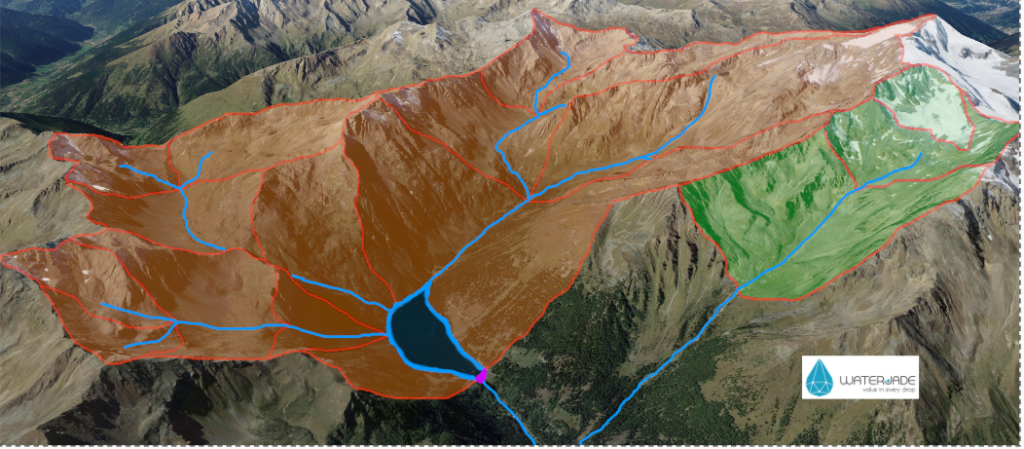
The workshop invited active participation of various stakeholders, including researchers, local authorities, irrigation consortia and energy utilities. Through collaborative exercises and discussions, participants explored scenarios related to drought, irrigation, and hydroelectric generation, shedding light on the multifaceted nature of water management challenges.
Towards a robust Decision Support System: Human and Digital challenges
Workshop participants noted that the issue of climate change must be assessed and approached holistically by finding the right cooperation and coordination between different sectors, such as agriculture and hydropower, to mitigate conflicts over water resources. It was also stated that improving communication and awareness regarding water usage and scarcity among citizens is vital.
Participants highlighted the significance of historical data in formulating effective strategies and identified areas for improvement, such as enhancing data accessibility, integrating data-sharing mechanisms and refining user interfaces to facilitate informed decision-making.
They also underscored the importance of user-friendly interfaces and clear instructions for navigating the DSS platform. Addressing language barriers and ensuring seamless accessibility were identified as crucial factors in optimizing user experience.
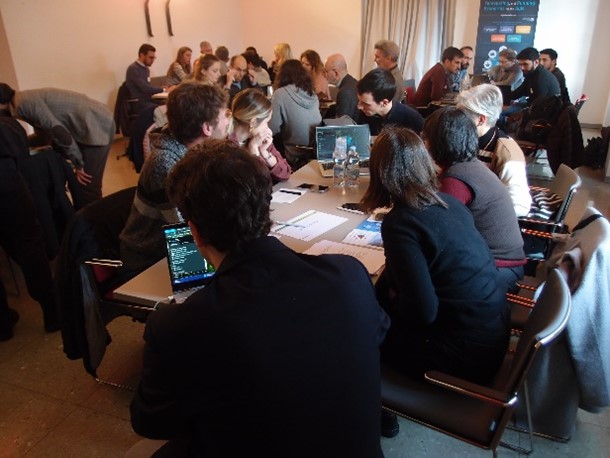
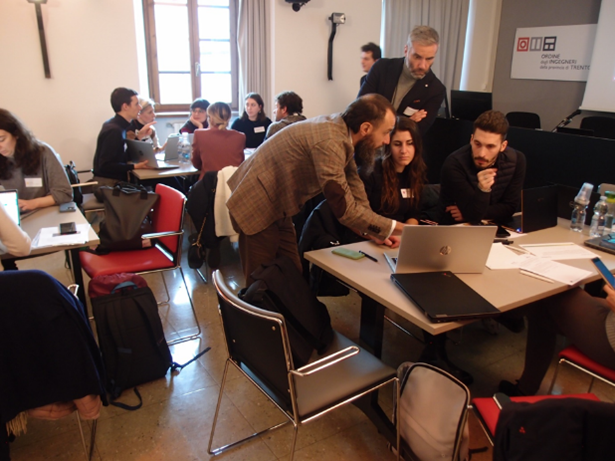


IMPETUS activities in the Valle dei laghi area are being carried out within the framework of the Water-Energy-Food-Ecosystem Nexus. The workshop provided a valuable opportunity for stakeholders to collaborate, exchange insights, and chart a course towards more sustainable water management practices. As the project continues to evolve, these collective efforts will play a pivotal role in safeguarding water resources for future generations.