Water flows through the Ebre Delta, nourishing both wildlife and agriculture. This vital region in southern Catalonia is home to one of Spain’s largest rivers, the Ebre, and supports both natural ecosystems and large-scale rice cultivation. However, this delicate balance between nature and agriculture is at risk, as rice farming introduces chemicals into the water, threatening the wetlands that surround the rice fields.
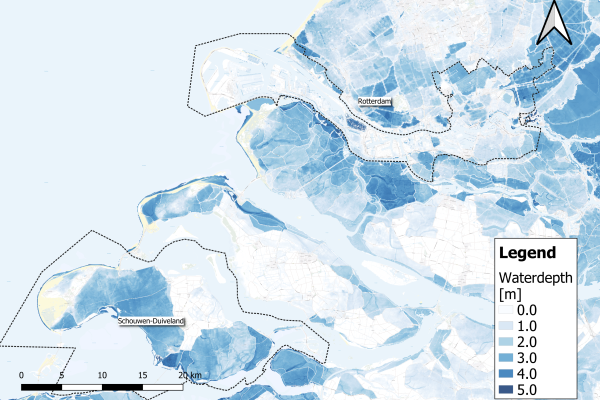
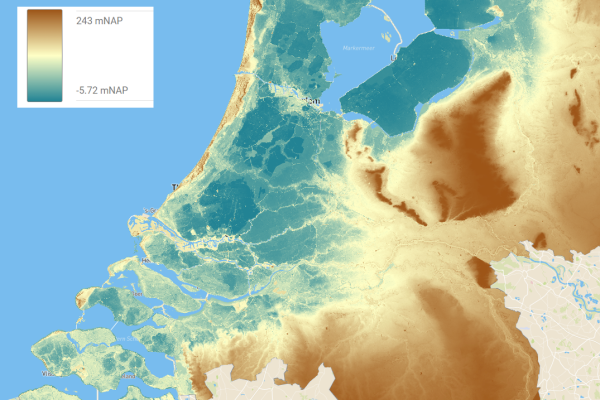
Wetlands, which cover only about 6% of the Earth’s land, are essential to life on our planet. They support around 40% of global wildlife and act as one of the largest carbon sinks. The Ebre Delta is no exception. Here, 10,000 hectares of wetlands lie adjacent to 22,000 hectares of rice fields, both of which depend heavily on the region’s water. The challenge, however, is managing the balance between rice farming, which requires significant irrigation, and protecting these crucial wetland ecosystems.
At the heart of the Delta, a network of 700 kilometers of irrigation canals delivers water diverted from the Ebro River to the rice fields. While this irrigation is essential for growing the 140 million kilos of rice harvested annually, it also leads to significant chemical runoff into nearby wetlands and the Mediterranean Sea. These chemicals, including pesticides and herbicides, not only threaten biodiversity but also impact the aquaculture industry along the coast, which produces over 3,400 tonnes of mussels and 300 tonnes of oysters each year.
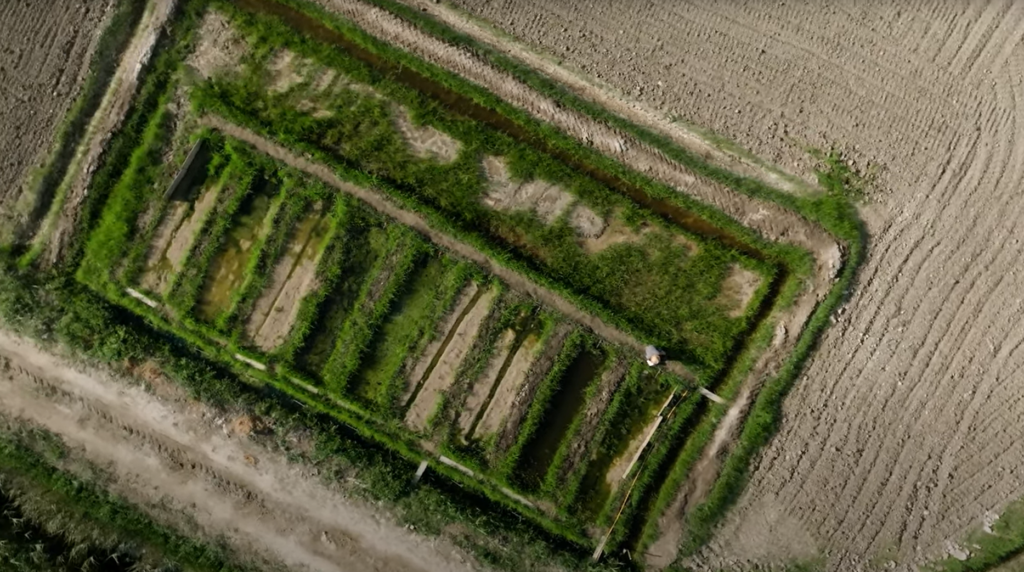
To address this issue, the IMPETUS project is testing an innovative solution: nature-based filtration systems to reduce the pollution leaving the rice fields. These systems, built at a pilot site in the Delta, are designed to slow down and filter water as it flows from the rice fields before it reaches the wetlands and sea. The project involves creating artificial wetland cells filled with natural absorbents like sand, biochar, and rice husks. These materials act as filters, removing contaminants from the water.
The IMPETUS researchers conducted laboratory experiments at Eurecat in Manresa to determine the best combination of materials for filtering water. The most promising mixture—biochar and sand—was able to remove 80 to 90% of contaminants in lab conditions. Following this success, the team installed the mixture at the Delta pilot site in April 2023, creating nine test cells, each filled with different absorbents, to compare their effectiveness under real field conditions.
Initial results from the pilot site show up to 60% removal of common fungicides and herbicides, a promising outcome given the challenges of filtering water in an open environment. While the removal rates were lower than in controlled laboratory conditions, the findings demonstrate significant potential for reducing the chemical load entering the wetlands and sea. The next step will be to validate these results under real field conditions, with the ultimate goal of developing scalable solutions that could be applied not only in the Ebre Delta but in other rice-growing regions around the world.
If successful, this innovative filtration method could revolutionize how we manage agricultural water runoff, protecting vital ecosystems while ensuring that farming can continue to thrive. The IMPETUS project’s pilot solution offers hope for a future where agriculture and nature can coexist in harmony, preserving biodiversity and ensuring cleaner water for generations to come.